- Home
- Experiments
- 1 - Voltage and Current of Solar Cells
Experiment 1: Voltage and Current of Solar Cells
What is a solar cell?
Photovoltaic (PV) cells are semiconductors which become electrically conductive on exposure to light or heat.
Solar cells can be divided into three groups based on raw material. Solar cells have an efficiency of about 10%.
-
Monocrystalline
Highly pure silicon melt is used to grow mono-crystals in the form of round silicon blocks. A mono-crystal’s lattice has an entirely homogeneous structure. The silicon block is sawed into wafers each 200 to 300 μm thick. -
Polycrystalline
Highly pure silicon melt is also used as the initial material for polycrystalline cells. These cells are manufactured through controlled cooling of the silicon melt in square-shaped moulds. During cooling, the crystals arrange themselves in an irregular pattern resulting in an iridescent surface typical of polycrystalline solar cells. -
Thin-film
-
Amorphous silicon cell
To manufacture amorphous solar cells, silicon is vapour-deposited on a carrier, e.g. glass. The vapour-deposited silicon layer has a thickness of 0.5 to 2 μm. - Copper-indium-diselenide cell (CIS).
- Gallium-arsenide (GaAs).
-
Amorphous silicon cell
A PV model can be expressed by the equivalent circuit shown in Figure 1.
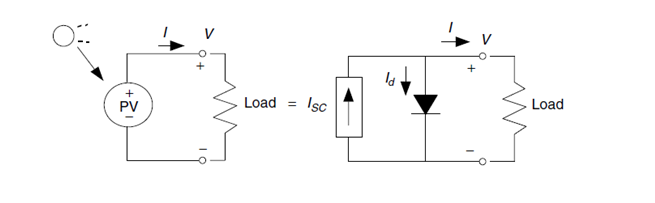
Figure 1. Equivalent circuit of a PV model
| Nominal Condidtion | Standard Condition |
|---|---|
| Irradiance = 800 W/m2 | Irradiance = 1000 W/m2 |
| Ambient temperature = 20℃ | Cell temperature = 25℃ |
| Wind speed = 1 m/s |
Open-circuit voltage of a solar cell
The open-circuit voltage VOC is the maximum voltage available from a solar cell.As the cell temperature increases, VOC decreases. VOC is measured using a volt meter connected across the solar cell when no load is connected, shown in Figure 2.
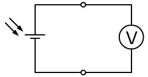
Figure 2. Measuring open-circuit voltage
Short-circuit current of a PV cell
The short-circuit current ISC is the maximum current a solar cell can supply. ISC is directly proportional to the irradiance. If irradiance increases, ISC will increase. If irradiance decreases, ISC will decrease. For example, if irradiance is cut in half, ISC will drop by half. The current is measured using an ammeter connected directly across the solar cell, shown in Figure 3
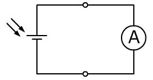
Figure 3. Measuring short-circuit current
- Measuring open-circuit voltage of solar cells
- Measuring short-circuit current of solar cells
- Solar Cells
- Voltage Meter
- Current Meter
- Connect a voltmeter to a solar cell with no load connected to it. Set the irradiance to 1000 W/m2, and temperature to 25℃. Record the open-circuit voltage VOC. Vary the cell temperature from 20 ℃ to 40 ℃ with the interval of 5 ℃ and keep the irradiance at 1000 W/m2. Record the open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current with different temperature in Table 1. Click on the button “Export table to CSV file” to save the data to an Excel file. How does VOC vary when the temperature increases?
- Connect an ammeter to a solar cell directly. Set the irradiance to 1000 W/m2, and temperature to 25℃. Measure the short-circuit current ISC. Vary the irradiance from 800 W/m2 to 1200 W/m2 with the interval of 100 W/m2, and keep the temperature constant at 25 ℃. Record the open-circuit voltage and short-circuit current with different irradiance in Table 2. Click on the button “Export table to CSV file” to save the data to an Excel file.How does ISC vary when the irradiance increases?
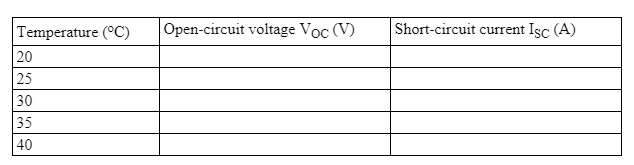
Table 1 VOC and ISC with the temperature variations
Table 2 VOC and ISC with the irradiance variations
- Fill out Table 1 with experimental data. How does VOC and ISC vary when the temperature increases?
- Fill out Table 2 with experimental data. How does VOC and ISC vary when irradiance increases?
Contact Us
Virtual Renewable Energy Laboratory
Principal Investigator:Liping Guo, Ph.D.
815-753-1350
lguo@niu.edu
Co-Principal Investigator:
Andrew W. Otieno, Ph.D.
815-753-1754
otieno@niu.edu
The project is funded by the
National Science Foundation
Improving Undergraduate STEM Education program (DUE-1712146)
from June 2017 to May 2020.
